What is a revision knee replacement?
Revision knee replacement surgery is a procedure in which a previously implanted prosthesis is revised or replaced with a new total knee implant. An original total knee implant has four components; femoral, tibial, plastic insert and patellar component.
A revision total knee replacement can be a revision of all the components or revision of one component, for example only change of polyethylene (plastic) liner.
Revision total knee replacement surgery is a demanding surgery, but the results are good in the vast majority of patients, though not as good as primary total knee replacement surgery.
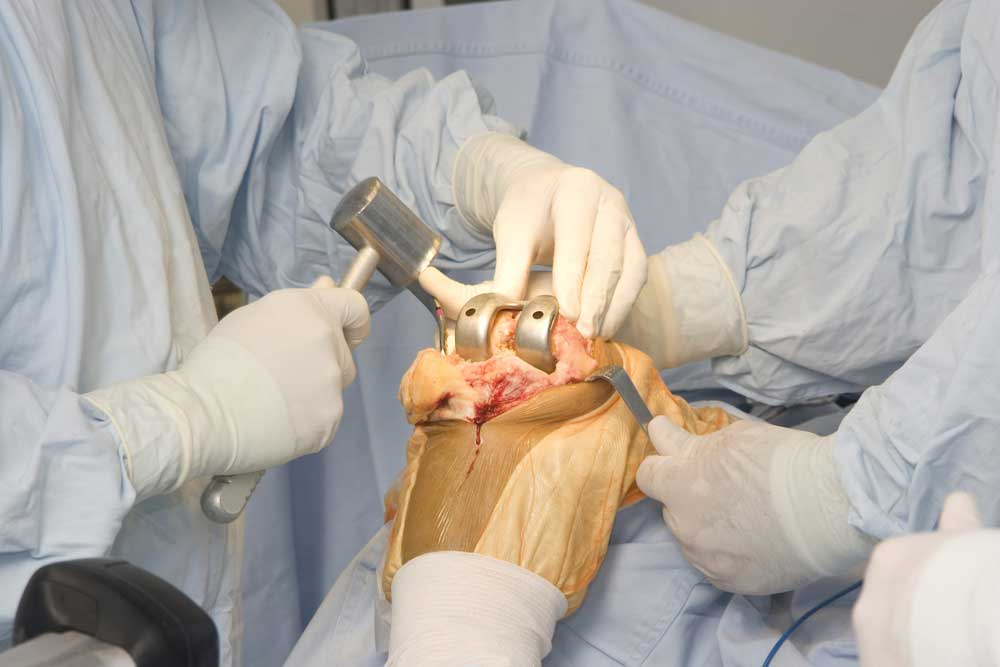
When is it needed?
Total knee replacement surgery is a highly successful surgery with a good long-term result of 95% at 15 yrs. It provides dramatic relief in pain, correction of deformity, improvement of functions and independence in the life of patients suffering with advance arthritis of the knee. Not only this surgery is being done in ever increasing numbers, but also it is now offered to younger and active individuals who subject there replaced knee joints to high demands, affecting its longevity and leading to failure.
A loose knee implant tends to be painful and unstable, therefore patients who wear out their prosthesis will require a revision knee replacement surgery. Approximately 5% to 10% of knees undergoing TKA will require revision within 10 to 15 years.
Knee replacements can wear out for a variety of reasons. Polyethylene wear has emerged as an important cause of TKA failure (aseptic loosening and Osteolysis (development of loose bone cavities around hip implant without loosening of implant)). The most common indications for revision TKA are infection, mechanical loosening, and instability. Dislocations, Periprosthetic Fractures (breaking of the bone around the prosthesis)
All revision total knee replacement other than for infection is done in single stage. In the case of infection, the primary implant may need to be removed to treat the infection, an antibiotic spacer need to be inserted along with few weeks of antibiotics, and once infection is controlled then revision knee replacement is performed.
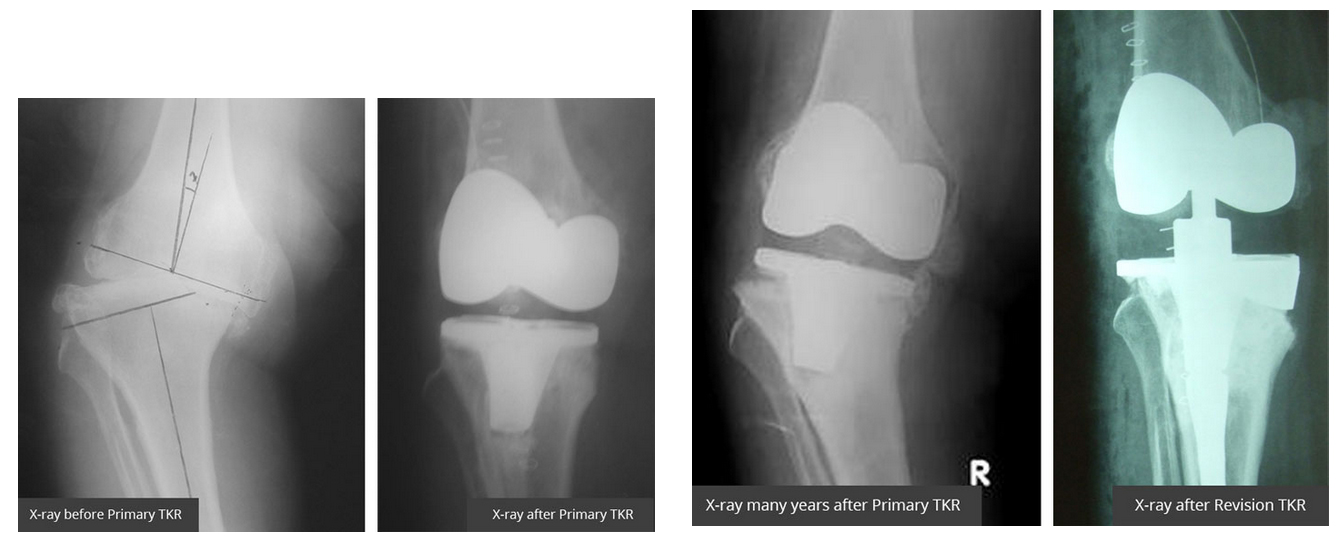
How do I know when I need revision surgery?
If your pain is increasing, if you are feeling instability or having difficulty in walking or you have to use a support for walking, if you are noticing loss of mobility in the knee joint, or there is continuous discharge from the operative scar not responding to any treatment, then its time for you to consult your doctor for the possibility of revision knee replacement
Sometimes may have few or no symptoms, but your x-rays show a big osteolysis next to the implant, which may be indicative of a need for revision surgery. Some other times you are very symptomatic, and x-rays also show gross malalignment or loosening of components or change in the position of components or you has sustained with periprosthetic fracture.
The decision and extent of revision knee replacement depends on severity of discomfort, x-rays, blood investigations like CRP or ESR and patients overall clinical condition. At times patient is required to undergo special investigations like Tc99 Bone scan / I111 bone scan or MRI to confirm the diagnosis. It is essential to remove a loose or damaged prosthesis before irreversible harm is done to the joint and surrounding bone.
Underlining the complex nature of surgery, the right time for revision knee surgery can be decided by you together with your Orthopedic surgeon in consultation with Physician and Anesthetist.
If you a revision knee surgery, you must discuss your options with your Orthopedic surgeon.
How revision total knee replacement can help me?
The revision total knee replacement surgery is a successful and durable operation, but not as much as primary total knee replacement surgery. You can expect significant improvement in your symptoms after revision knee surgery, which includes:
- Significant relief in pain
- Restoration of knee movements
- Stable joint
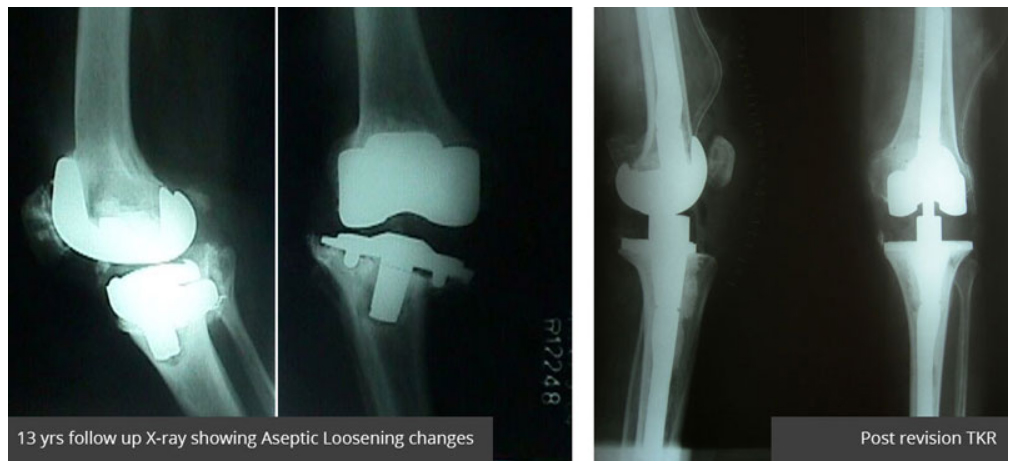
How different is revision knee surgery different than primary total knee replacement?
The principles of revision TKA are similar to those of primary surgery. However, revision knee surgery is more challenging and complicated than primary knee replacement. Poor quality of the patients bone often makes it difficult to achieve stable fixation of revision knee implants. Furthermore, removing the previous knee implants not only necessitates more extensive surgery, but also adds to loss of bone to the already limited patient bone stock.
Also not only do the patients tend to be older, but also the surgery time is longer and the blood loss is greater during or after surgery adding to the difficulty of revision surgery. Together, these problems make revision knee replacement much more complex surgery.
Revision knee surgery on an infected knee requires two or more separate operations. In the first operation, the old knee prosthesis is taken out and a block of cement mixed with high dose of antibiotics (antibiotic spacer block) is inserted in the joint for 6 - 12 weeks. This block acts as a spacer and also releases high concentration of antibiotics in the knee joint locally. The patient is also given intravenous antibiotics for 6 weeks, and constantly evaluated with repeated TLC, DLC, CRP and ESR. After the infection has cleared, the knee is reopened and the new revision prosthesis is implanted.
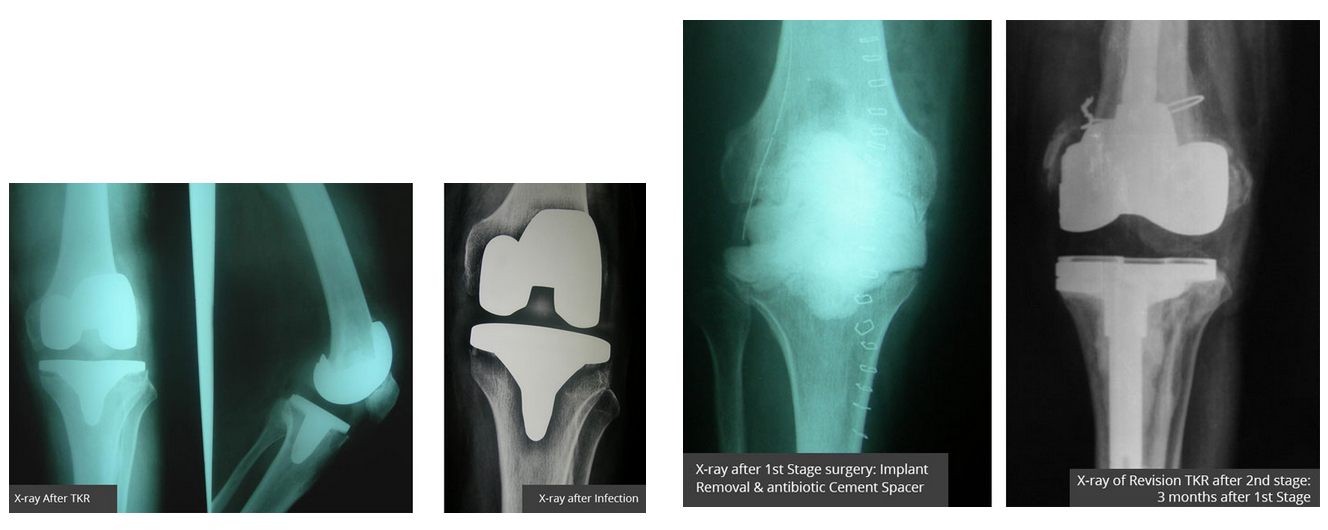
A case example of Management of infected TKR
During the revision surgery one may need special implant like constraint knees or rotating hinge with wedges, blocks, cone sleeves, extension rods, etc. Though these implants are expensive and have some limitations, but indispensable (in certain situation) to achieve good stability of revision implant.
What should I expect during my hospital stay?
Before Surgery: Most of the patients are admitted two days before surgery and undergo a through medical checkup which includes evaluation by the treating surgeon, anesthetist, intensivist, and physiotherapist besides investigations like Chest X-rays, ECG, blood (including CRP, ESR, TLC & DLC) and urine test. X-ray images of knees from different angles are taken to plan your surgery. You may require whole body bone scan or MRI of the knee. At least 2 – 3 units of blood may be necessary. Careful control of blood sugar is done before surgery.
Knees are scrubbed with soap and water, painted with betadine solution, and then covered with a sterile drape in your room a night before your operation.
Surgery: Preferable choice of anesthesia is Spinal anesthesia (it anesthetize both legs only) with sedation. The duration of surgery ranges from 2 to 3 hrs. You will be kept in a recovery room for one day for the monitoring of vital parameters. Knee bending is started on an exercise machine after 2-3 days of operation.
After Surgery: On the 3rd day your drainage tubes will be removed while on 4th day your dressing will be changed. In most cases a knee immobilizer will be worn. Knee bending on the CPM machine is started 2-3 days after surgery; bedside sitting is started on the 4th day while walking with support and toilet training are started from 5th day onwards.
Most patients can ambulate comfortably with the support of a stick or walker, bend knee up to 800 to 900, start going to toilet and are also able to climb a flight of stairs. Most patients are comfortably discharged on 8th to 10th day.
What happens after I go home?
Aftercare following knee revision surgery is essentially the same as for knee replacement, consisting of a combination of physical therapy, rehabilitation exercises, pain medication when necessary, and a period of home health care or assistance.
You will be requiring antibiotics for a longer time as compare to primary total knee replacement surgery especially if you are a diabetic, rheumatoid arthritis patient or infection was the cause of revision knee surgery.
The recovery time after revision knee replacement surgery depends on the cause of revision and may vary from 4 to 8 weeks.
What are the risk following Revision Total Knee Replacement?
The complications following revision knee surgery are similar to those for knee replacement and include:
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Infection in the new prosthesis: Incidence of reinfection following revision total knee replacement are higher in comparison to primary total knee replacement especially in diabetic and rheumatoid arthritis patient or if revision surgery has been done for infection of primary knee.
- Loosening of the new prosthesis. The risk of this complication is increased considerably if the patient is overweight.
- Bone fractures during the operation. These are caused by the force or pressure that the surgeon must sometimes apply to remove the old prosthesis and the cement that may be attached to it.
- Dislocation of the new prosthesis. The risk of dislocation is twice as great for revision surgery as for TKR.
- Formation of heterotopic bone. Heterotopic bone is bone that develops at the lower end of the femur following knee replacement or knee revision surgery. Patients who have had an infection in the joint are an increased risk of heterotopic bone formation.

 Menu
Menu